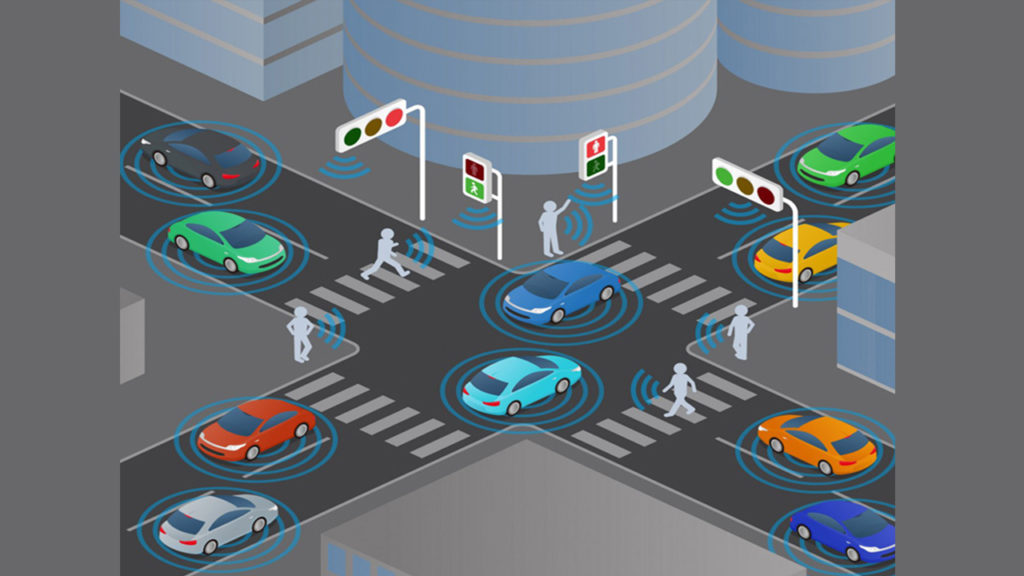
Systems that are not associated with other intersections located near an intersection is called isolated signalization systems. In other words, it can be described as the systems that an intersection controlled alone. In isolated systems, it is recommended that the periods should be as short as possible. However, periods are increased naturally if the traffic volume is high. This form of control may include fixed times based on prior observations or it may include different signal plans with fixed duration assigned according to the change in traffic flows during the day. These control systems are explained below titles.
Isolated signalization systems can be controlled as four different ways.
1. Fixed-time Signalization Control Systems
2. Traffic Actuated Signalization Control System
3. Pedestrian Actuated Signalization Control System
4. Adaptive Signalization Control System
1.Fixed Time Signalization Control System
Period, phase duration, phase numbers and range are predetermined at fixed time signalization control system. In the system, the right of way is given in sequence in accordance with the pre-prepared time schedules according to the vehicle and pedestrian traffic approaching the intersection from different directions. Fixed-time signalling systems can be implemented in two ways: One program during the entire day or the implementation of different programs during the day. In today’s traffic conditions, it is not suitable to implement same programme at all day. However, it is implemented time by time. Green durations which is given to traffic that approach the intersection from different ways and the ratio of these durations to each other is determined according to average traffic load at fixed time signalization control systems. Therefore, traffic counts need to be done in large numbers and carefully for the success of the system.
In general, it is possible to describe the process in four stages. First stage is data collection. An exercise should be done for designed intersection including all details. In this context, including peak and off-peak, hourly traffic volume data, pedestrian traffic data and accident data at each intersection should be gathered by determining intersection geometry and location. In addition, the information of stop and pocket should be gathered which belongs to the public transportation systems near the intersection. External elements that may affect intersection inspection performance in relation to the location of the intersection (e.g. loading and unloading activities in commercial areas, land topography, etc.)) must be noted. When collecting vehicle traffic volume data, traffic composition and manoeuvre patterns (right and left turn ratios) should also be considered. In the second phase, according to the data collected, the intersection must be analysed. The sufficiency of existing data must be evaluated. At this stage, Webster or Australian methods can be used for analysis. The Webster signal design method can be effectively used if the usage rate at the intersection is 0.9 and below. However, it would be appropriate to use the Australian signal design method to make the capacity utilization rate 0.9 and above. According to the selected analysis method, the intersection is analysed and the signal times to be applied are determined. The performance of the intersection is evaluated according to the applied signal times at the end of the analysis. For this purpose, the delay parameter is considered as the performance criterion. The delay of each current at the intersection correspondingly the intersection delay times are calculated. The service level corresponding to the intersection delay time is determined and evaluated. After the evaluation, if it is decided that the design is suitable, field application is initiated. For important and critical projects, field analyses are done after the field application. Therefore, the suitability of work tested. If it is not suitable, a new design developed. The final decision can be made by making calculations using software developed for the design of this system.